Automotive
Automotive Application - HEV Main Inverter
Electronic power train control is key to fuel efficiency and lower emissions. The main inverter converts high voltage, high current DC to AC (the electric traction motor is a 3-phase AC load.) The main inverter controls the electric motor. The electronics in a main inverter are ideally designed to minimize switching losses and maximize thermal efficiency. The range of an electric vehicle is related to the efficiency of the main inverter. Efficiency is dependent upon the electronics in the inverter. The components should be able to withstand extremely high temperatures (125°C) and be as small and light as possible via means of better packaging or integration of external components to reduce overall part count.
Efficient power electronics with high-frequency switching and high resolution PWM control are desirable, and lead to smaller, more power-dense designs that require fewer/smaller passives. IGBT or IGBT modules are preferred for higher currents in typical inverter applications, although MOSFETs are also capable of handling medium levels of power and overlap in functionality somewhat. Power density in semiconductors has nearly doubled since 1995. However, Silicon Carbide (SiC)-based substrates are fairly new and hold even more promise with power density at higher switching frequencies and with better thermal characteristics.
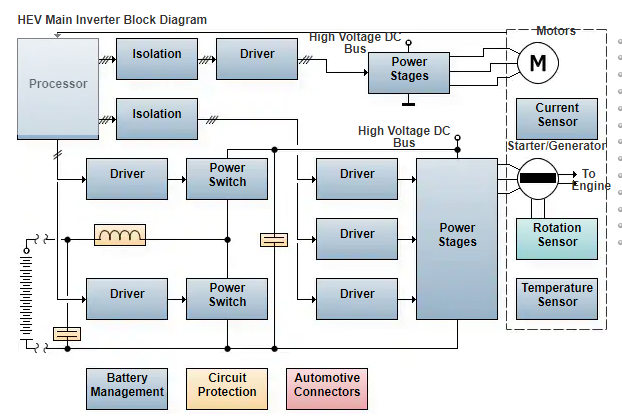
This design is for reference only. The design, as well as the products suggested, has not been tested for compatibility or interoperability.